SNA #2: SSL PROXY PROCESS
Todays topic:
Understanding The SSL PROXY PROCESS
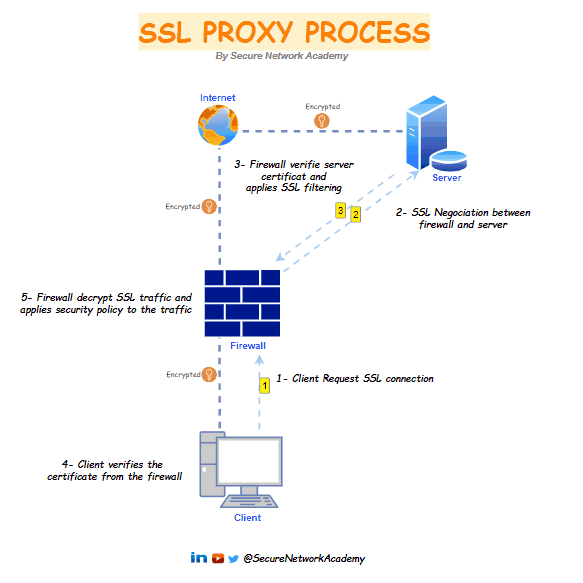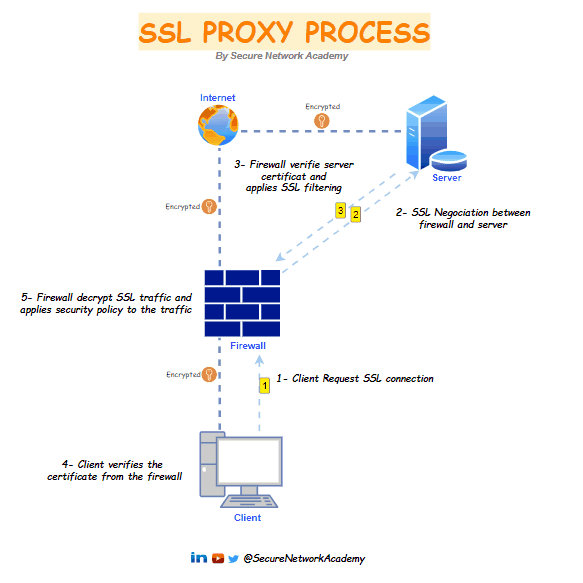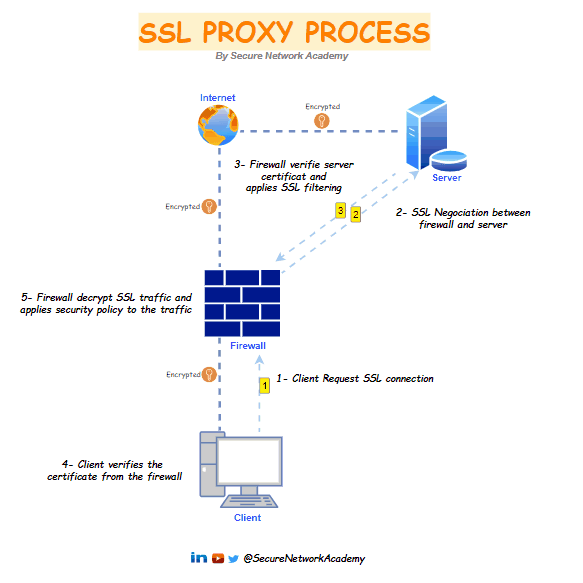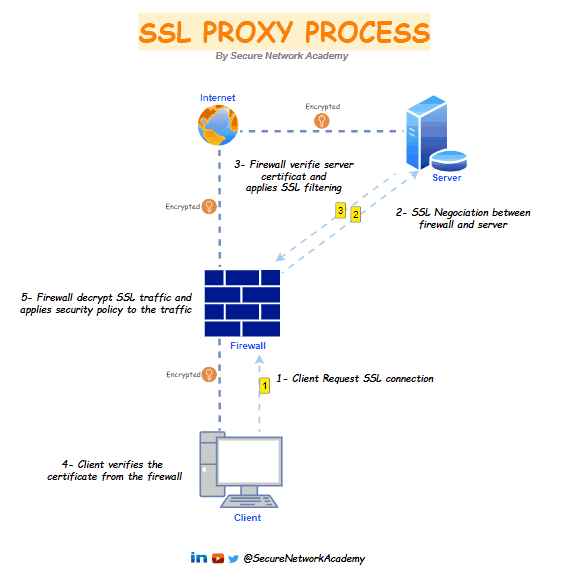
The SSL proxy is positioned as a "man in the middle" on SSL traffic between the client and the web server. It handles SSL negotiations, securing both SSL proxy-to-server and SSL proxy-to-client connections. In this role, it allows or restricts connections according to filtering policies and, when required, decrypts SSL data.
This figure provides a detailed illustration of the synchronization process
1- The SSL proxy intercepts client connections and initiates a TLS session with the external server on behalf of the client.
2- The server sends a signed certificate to the SSL proxy.
3- The SSL proxy verifies the server certificate, if the certificate is compliant. the firewall generates copy of the server certificate and sends it to the client.
4- SSL traffic flows through the firewall, where it is decrypted, filtered, re-encrypted, and then forwarded to its destination.
5- The client verifies the firewall certificate and initiates a session key exchange with the server; The client and server exchange keys through the firewall, and the firewall acts as an invisible intermediary. There are two separate sessions: one between the client and the firewall and another between the firewall and the server. Now, everyone has the necessary certificates and keys, allowing the firewall to decrypt the traffic.
6- All SSL session traffic between goes through the firewall transparently between the client and the server. The firewall decrypts the SSL traffic, applies security policies and profiles and decryption profiles to the traffic, re-encrypts the traffic, and then forwards it.